Whether you’re driving a car, ATV, or an electric golf cart, your four-wheeler’s battery plays a critical role in performance, reliability, and safety. Understanding the different types of four-wheeler batteries and how to choose and maintain them can help extend battery life and prevent unexpected breakdowns. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about four-wheeler batteries.
Understanding Four-Wheeler Batteries
A four-wheeler battery serves as the heart of the vehicle’s electrical system. It powers everything from the ignition system and starter motor to the lights, infotainment, and more. With growing advancements in vehicle technology, battery performance has become more crucial than ever.
Key Components of a Four-Wheeler Battery
- Electrolyte – The medium that allows the flow of electric charge between the plates.
- Positive and Negative Plates – Made of lead-based materials, these plates store and discharge electricity.
- Separator – Prevents the plates from touching and short-circuiting while allowing ionic movement.
- Battery Case – Typically made of polypropylene, it houses the internal components and protects them from external damage.
- Terminals – Provide the connection point between the battery and the vehicle’s electrical system.
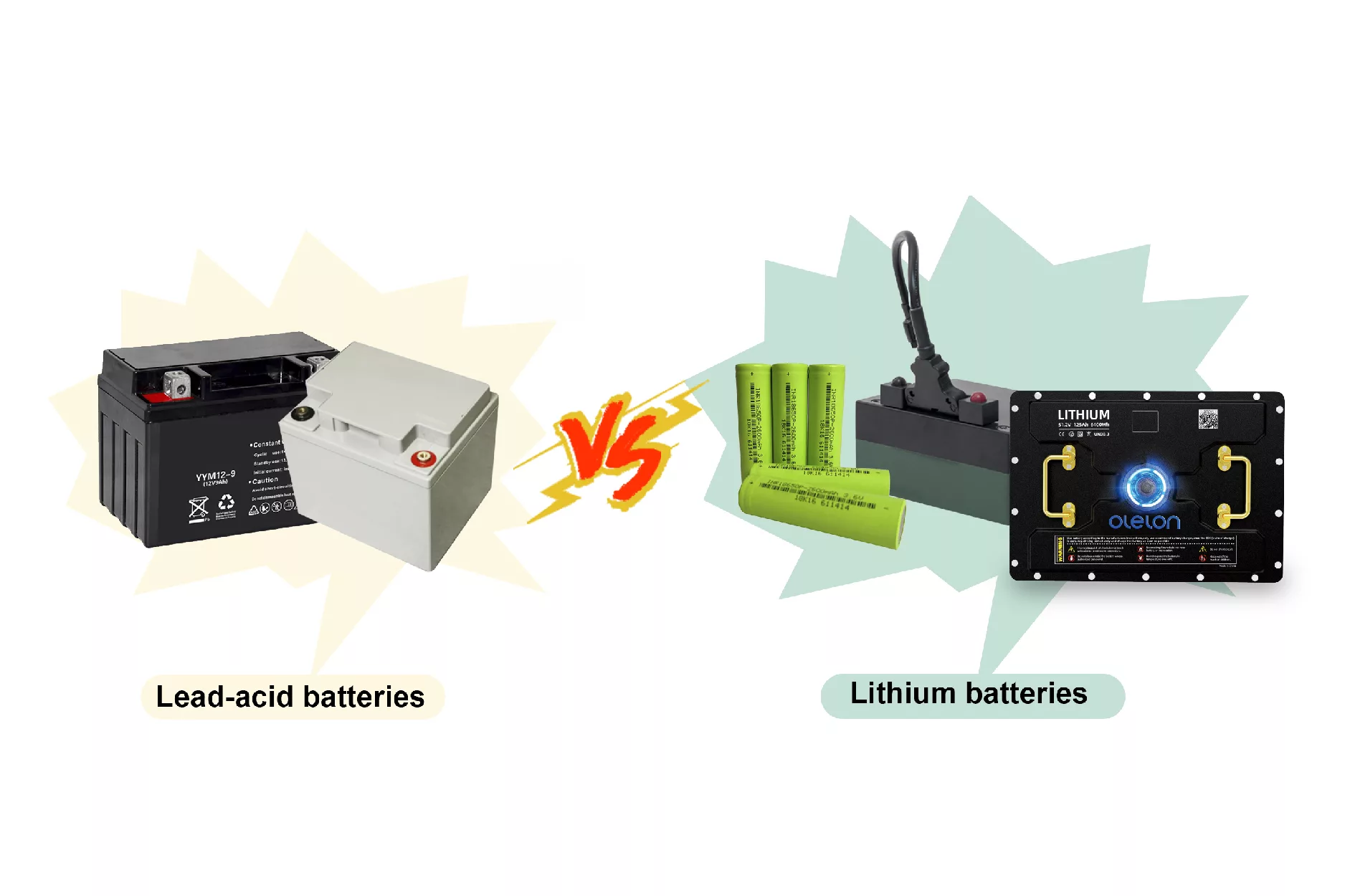
Types of Four-Wheeler Batteries
1. Lead-Acid Batteries
These traditional batteries are affordable and widely used in standard vehicles. They require regular maintenance and water top-ups but offer a reliable performance for basic vehicle needs.
2. Absorbent Glass Mat (AGM) Batteries
AGM batteries use a fiberglass mat to absorb the electrolyte. They are spill-proof, maintenance-free, and provide better vibration resistance, making them ideal for off-road vehicles and modern vehicles with high power demands.
3. Lithium-Ion Batteries
Known for their lightweight design and long lifespan, lithium-ion batteries are becoming increasingly popular in electric vehicles and high-performance applications. They offer fast charging, deep discharge cycles, and require minimal maintenance.
4. Gel Batteries
Gel batteries use a silica-based gel as the electrolyte, making them spill-proof and resistant to extreme temperatures. They’re suitable for deep-cycle applications and environments with high vibration.
How to Choose the Right Battery for Your Four-Wheeler
1. Compatibility
Always select a battery that matches your vehicle’s specifications. Check your owner’s manual for recommended voltage, capacity, and dimensions.
2. Cold Cranking Amps (CCA)
This rating indicates how well the battery performs in cold temperatures. Higher CCA ratings are essential for vehicles in colder climates.
3. Reserve Capacity (RC)
RC measures how long the battery can supply power if the alternator fails. A higher RC offers greater peace of mind during emergencies.
4. Warranty
Look for batteries with strong warranties to ensure quality and long-term support.
Maintenance Tips for Four-Wheeler Batteries
1. Regular Inspections
Check for corrosion, loose connections, and physical damage. Clean the terminals periodically.
2. Monitor Electrolyte Levels
For lead-acid batteries, ensure that electrolyte levels are adequate. Top off with distilled water if needed.
3. Keep the Battery Charged
Avoid letting your battery discharge completely. Use a battery maintainer if your vehicle isn’t used regularly.
4. Temperature Considerations
Extreme heat and cold can reduce battery life. Store your vehicle in a climate-controlled garage when possible.
Conclusion
Choosing the right battery and maintaining it properly is essential for the reliable performance of your four-wheeler. Whether you opt for a classic lead-acid battery or a cutting-edge lithium-ion option, understanding your needs and the technology available will ensure your vehicle runs smoothly for years to come.
Example Application:
This guide applies to various types of four-wheelers—from passenger cars to electric golf carts like the one below. Choosing the right battery can significantly affect your vehicle’s lifespan, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.
Comparison Chart Example:
| Battery Type | Maintenance | Lifespan | Vibration Resistance | Cold Weather Performance | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lead-Acid | High | 3-5 years | Low | Medium | Low |
| AGM | Low | 4-6 years | High | High | Medium |
| Lithium-Ion | Very Low | 8-10 years | Very High | Excellent | High |
| Gel | Low | 4-6 years | High | Good | Medium |

