Introduction
As the demand for clean energy grows, LiFePO4 (Lithium Iron Phosphate) batteries have become a popular choice across industries due to their high safety, long cycle life, and eco-friendliness. To meet varying application needs, LiFePO4 batteries come in multiple structural formats. This article introduces the main types of LiFePO4 battery cells and explains their characteristics, applications, and advantages.
Different Types of LiFePO4 Batteries
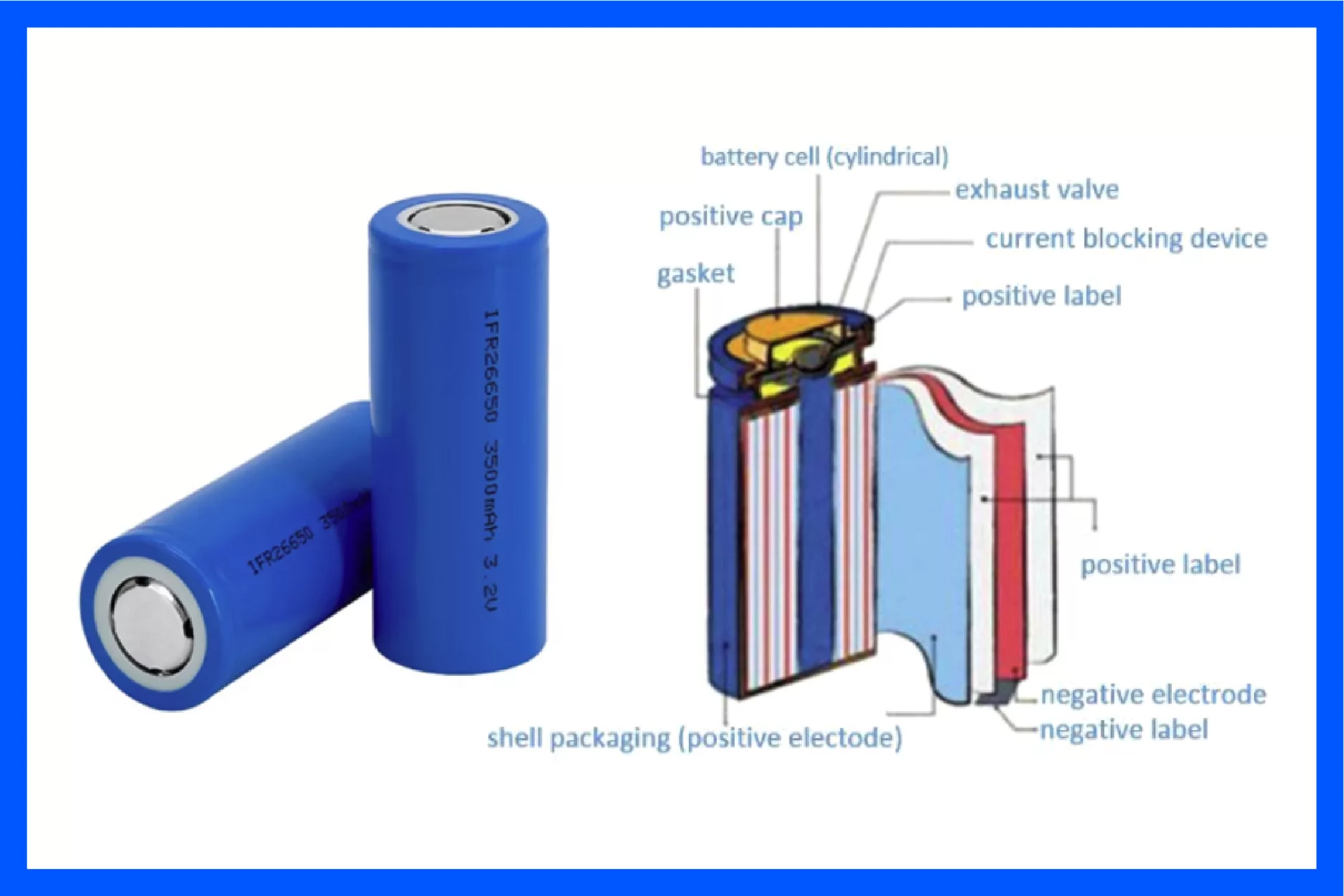
Cylindrical Cells
Cylindrical cells are one of the most established formats, known for their excellent consistency, high mechanical strength, and good heat dissipation. Commonly used in power tools, electric bikes, and small energy storage systems.
Key Features:
- Standardized sizes (e.g., 18650, 21700)
- Low production cost
- High automation efficiency
Prismatic Cells

Prismatic cells feature a rigid aluminum case and compact structure, offering higher space utilization. They are widely used in electric vehicles and machinery where space is tight and high energy is required.
Key Features:
- Large capacity and space efficiency
- Good thermal performance
- Flexible battery pack design
Pouch Cells
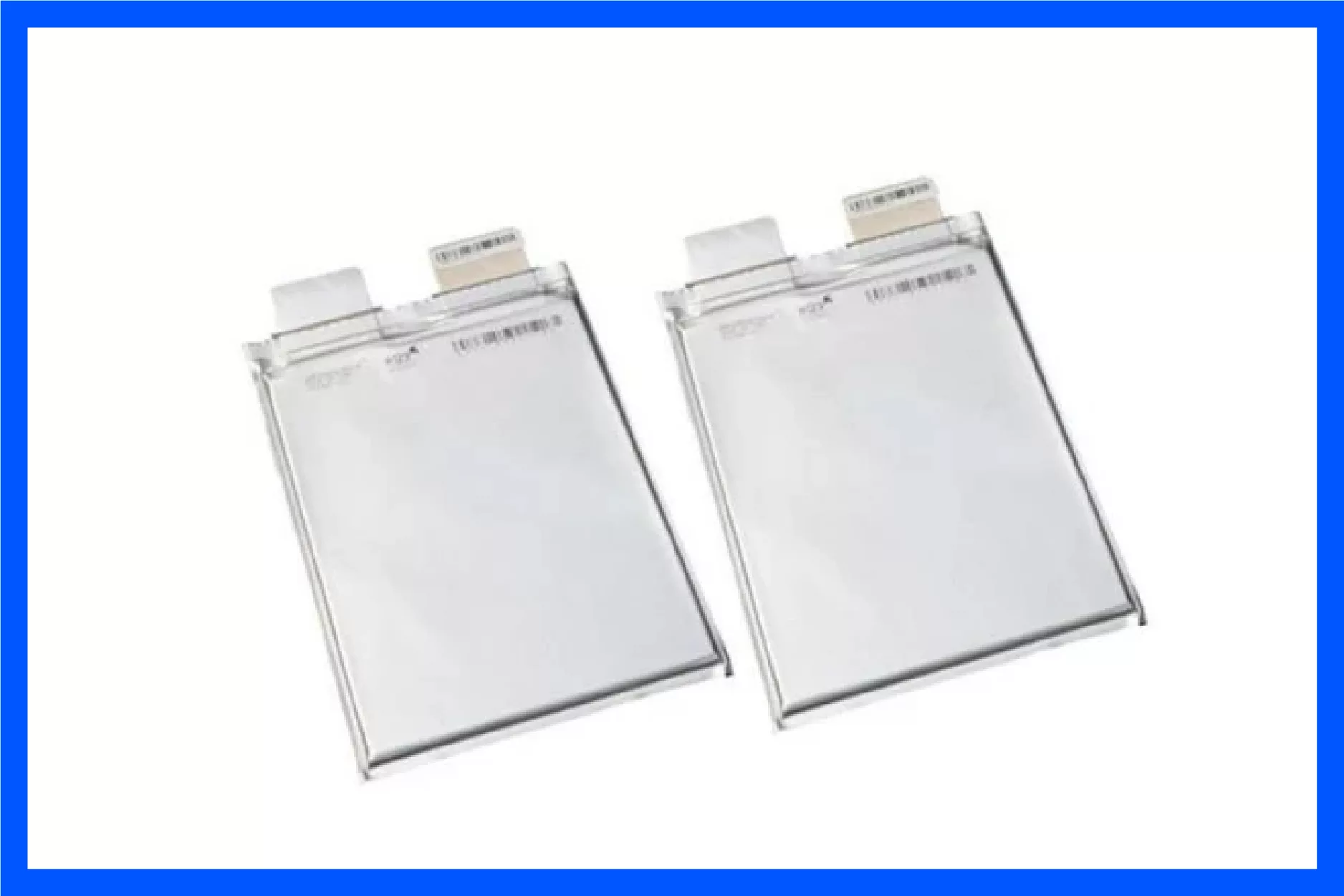

Pouch cells use a lightweight aluminum-plastic film, allowing for flexible shapes and higher energy density. They are commonly used in portable electronics, e-motorcycles, and custom battery packs.
Key Features:
- Lightweight and flexible
- High energy density
- Higher cost compared to cylindrical/prismatic
Large-Format Cells
Large-format LiFePO4 cells are designed for high-capacity applications such as energy storage systems, commercial EVs, and industrial equipment. They offer higher voltage platforms and longer cycle life.
Key Features:
- High single-cell capacity (typically 100Ah to 300Ah+)
- Simplified system integration
- Lower maintenance costs
Detailed Comparison
| Type | Structure | Typical Capacity Range | Typical Applications | Relative Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cylindrical | Round metal casing | 1Ah – 5Ah | Power tools, e-bikes | Low |
| Prismatic | Hard aluminum case | 10Ah – 100Ah+ | EVs, industrial machinery | Medium |
| Pouch | Flexible pouch | 5Ah – 50Ah | Portable devices, e-motorcycles | Medium–High |
| Large-Format | Varies (large size) | 100Ah – 300Ah+ | Energy storage, electric buses | High |
Applications of LiFePO4 Batteries
- 🔋 Electric Vehicles (cars, buses, trucks)
- 🌞 Energy Storage Systems (home solar, grid-level storage)
- 🔧 Power Tools (cordless drills, lawn mowers)
- 📱 Consumer Electronics (portable power stations, UPS)
- 🚜 Industrial Equipment (AGVs, forklifts, rail systems)
Advantages of LiFePO4 Batteries
- ✅ High Safety: Excellent thermal and chemical stability, minimal fire risk
- 🔁 Long Cycle Life: Up to 3,000–6,000+ cycles
- 🌱 Environmentally Friendly: No heavy metals, high recyclability
- ⚡ Stable Power Output: Flat voltage curve ensures steady performance
- 🛠️ Low Maintenance: Minimal upkeep, suitable for long-term use
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: How do LiFePO4 batteries compare to NMC (ternary lithium) batteries?
A1: LiFePO4 batteries offer better safety and longer lifespan, while NMC batteries have higher energy density. Choose based on whether your priority is safety/longevity or range/compactness.
Q2: Why use large-format cells for energy storage?
A2: Fewer connections, better stability, and easier integration make large cells ideal for large-scale energy applications.
Q3: Are pouch cells prone to swelling or damage?
A3: Pouch cells require proper structural support and thermal management. When used correctly, they offer excellent performance in lightweight and compact systems.