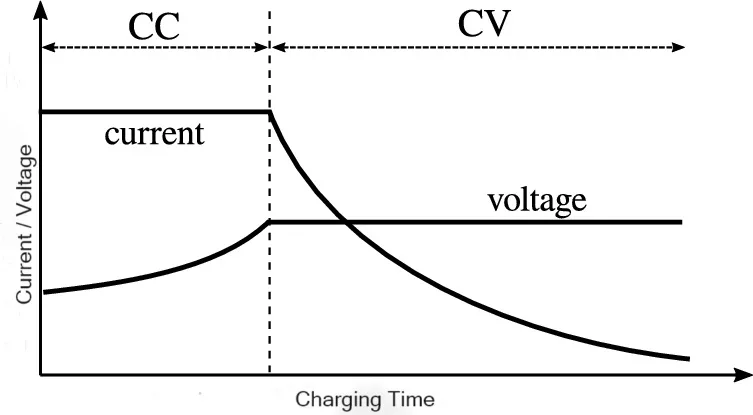
1. Charge Method: CC/CV (Constant Current/Constant Voltage)
- Definition: CC/CV is a common charging method for lithium-ion batteries. It involves two stages:
- Constant Current (CC): The charger supplies a constant current to the battery until it reaches a specific voltage.
- Constant Voltage (CV): Once the battery reaches the target voltage, the charger switches to supplying a constant voltage while the current gradually decreases until the battery is fully charged.
- Benefits: This method ensures efficient and safe charging, preventing overcharging and extending battery life.
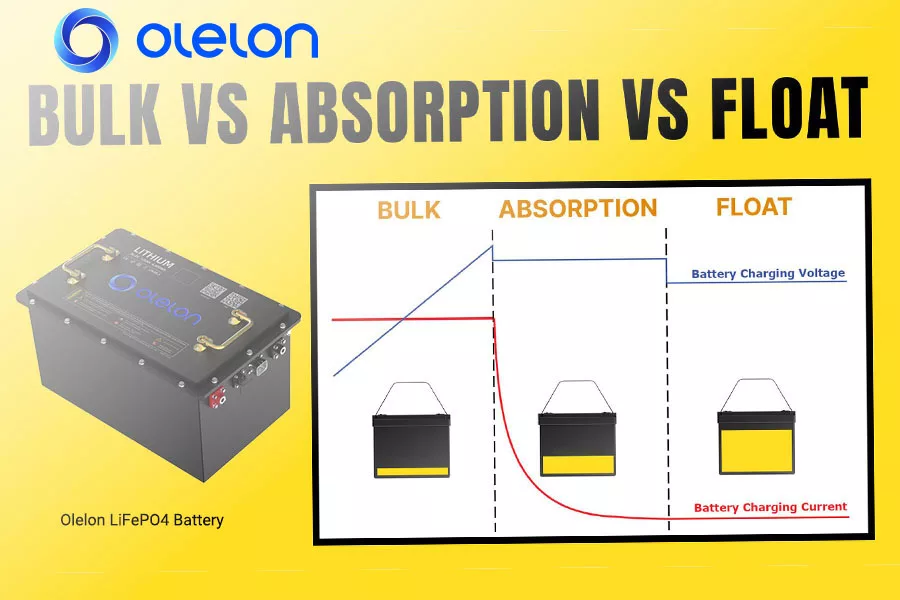
2. Bulk, Absorb, Float Charging Stages
- Bulk Charge: The initial stage where the charger delivers maximum current to rapidly charge the battery until it reaches a set voltage.
- Absorb Charge: The charger maintains a constant voltage while the current decreases, allowing the battery to absorb the remaining charge without overheating.
- Float Charge: The charger provides a lower, constant voltage to keep the battery fully charged and compensate for self-discharge, ensuring the battery is ready for use at any time.
3. Why Some Rechargeable Batteries Require Manufacturer’s Chargers
- Compatibility: Manufacturer’s chargers are specifically designed to match the battery’s chemistry, voltage, and current requirements, ensuring optimal performance and safety.
- Protection: These chargers often include built-in safety features such as overcharge protection, temperature monitoring, and short-circuit prevention, which generic chargers may lack.
- Warranty: Using the manufacturer’s charger can help maintain the battery’s warranty, as using third-party chargers might void it due to potential risks of damage or reduced performance.
These charging methods and requirements is crucial for maintaining battery health, ensuring safety, and maximizing the lifespan of your rechargeable batteries.